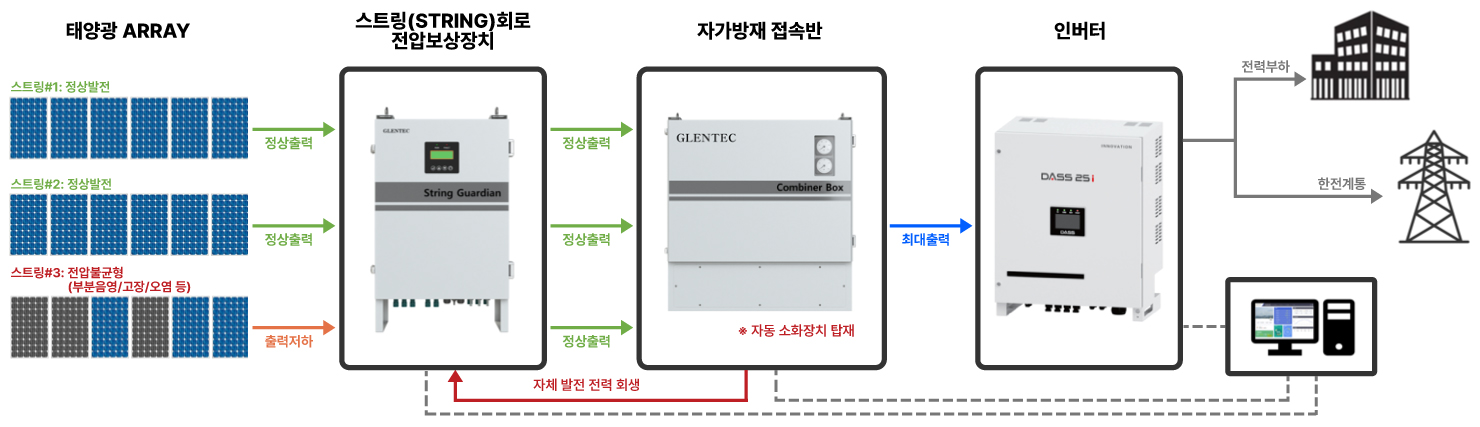
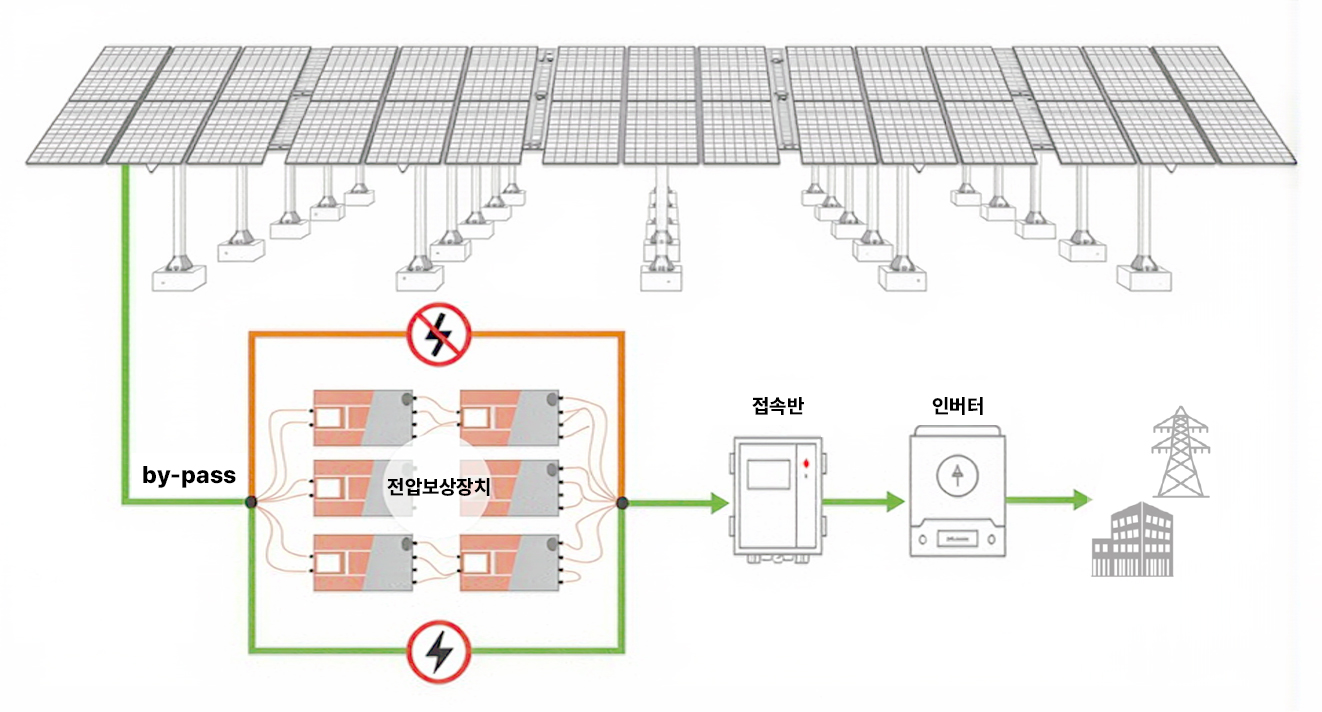
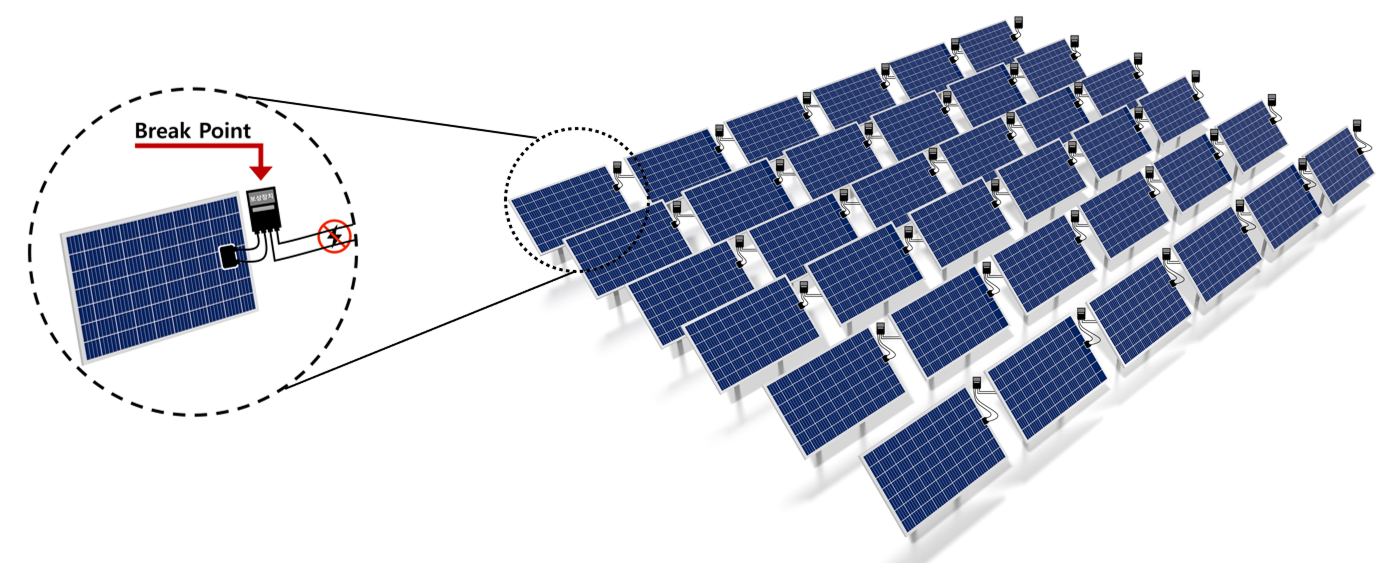
Fire at Incheon concert hall construction site PV facility, November 2019
According to Incheon Seobu Fire Station, a fire broke out at around 2:50 p.m. on the 26th at the Cheongna Complex Culture Center concert hall construction site in Gyungseo-dong, Seo-gu, and was extinguished about 50 minutes later at 3:40 p.m. The fire damaged the two-story building rooftop (165㎡) and PV modules, with property damage estimated by the fire station at about 130 million won.